Improving a virus’s cancer-killing potency

Rahman Masmudur is a researcher with the Biodesign Center for Immunotherapy, Vaccines and Virotherapy at ASU.
In recent years, an unusual new domain in cancer research has opened up. The idea is to use infectious pathogens to attack and kill cancerous cells. So-called oncolytic viruses, in particular, have shown great promise for targeting cancer cells while leaving normal, healthy cells intact.
In new research, Rahman Masmudur and his colleagues describe a method for improving the effectiveness of a powerful oncolytic virus known as myxoma virus.
A member of the pox family of viruses, myxoma virus has some highly unusual properties. It has long been recognized as lethal to European rabbits, producing an invariably fatal disease known as myxomatosis, while appearing harmless to other species, including humans. Remarkably, myxoma virus has more recently been shown to display an insatiable appetite for cancer cells, attacking and killing them.
“We are trying to improve myxoma virus’s ability for infection, replication and killing different types of human cancer cells,” Masmudur said. “We are doing it by identifying and targeting the cellular proteins that restrict myxoma virus replication in human cancer cells.”
Masmudur is a researcher with the Biodesign Center for Immunotherapy, Vaccines and Virotherapy at ASU. The new study was spearheaded by co-corresponding author Grant McFadden, who directs the center and is a leading authority on the myxoma virus and its oncolytic potential.
The new research appears in the Journal of Virology, which has highlighted the new study in its Spotlight section, reserved for especially meritorious articles.
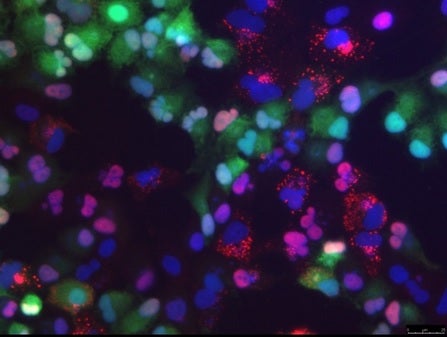
Antiviral granules (seen in red) sprayed into the cytoplasm by the protein DHX9. These granules act to inhibit the virus-fighting capacity of the myxoma virus, which is being explored as a therapy to treat cancer.
Scientists are hoping to design a range of new cancer therapies, based on oncolytic viruses such as myxoma. One challenge in advancing such research is the fact that certain cancers, known for their many-faceted efforts to resist effective therapy, can outwit myxoma virus by using an anti-viral cellular component called RNA helicase A/DHX9.
RNA helicases are members of a large family of proteins considered crucial for RNA metabolism and gene expression. RNA helicase A/DHX9 has been shown to reduce the effectiveness of myxoma virus against cancer cells. It does this by forming anti-viral granules in the cancer cell’s cytoplasm, inhibiting the myxoma virus’s ability to replicate.
The new research identifies the RNA helicase A/DHX9 protein as a potential target for new therapies that could neutralize its antiviral properties, thus improving the cancer-fighting potential of myxoma and other oncolytic viruses.
More Science and technology

4 ASU researchers named senior members of the National Academy of Inventors
The National Academy of Inventors recently named four Arizona State University researchers as senior members to the prestigious…

Transforming Arizona’s highways for a smoother drive
Imagine you’re driving down a smooth stretch of road. Your tires have firm traction. There are no potholes you need to swerve to…

The Sun Devil who revolutionized kitty litter
If you have a cat, there’s a good chance you’re benefiting from the work of an Arizona State University alumna. In honor of…

