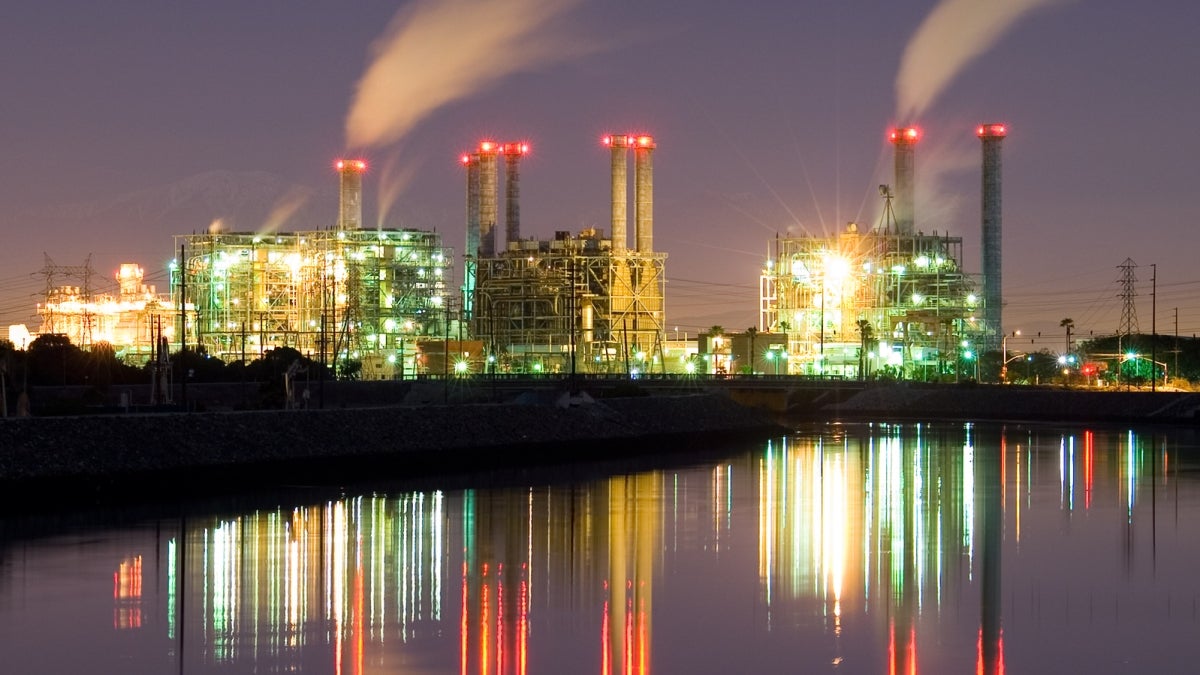
Federal data on power-plant carbon dioxide emissions is significantly flawed, according to a study by Arizona State University scientists published this month.
Monthly emission differences at a fifth of U.S. power plants varied plus or minus 13 percent. At half the plants, differences varied plus or minus 6 percent.
Inaccurate data undermines the federal Clean Power Plan, which is designed to strengthen the trend of clean energy by setting a national limit on carbon pollution produced from power plants.
“I would say that, in order for that piece of policy to be as effective as I’m assuming everyone wants, we need to make sure we’re monitoring and measuring power plants accurately,” said Kevin Gurney, lead author of the study. GurneyGurney is a senior sustainability scientist in the Julie Ann Wrigley Global Institute of Sustainability and an associate professor in the School of Life Sciences in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences. is an atmospheric scientist, ecologist and policy expert working in carbon-cycle science, climate science, and climate-science policy.
Gurney (left) was “pretty darn surprised” by the findings.
“That’s too much error,” he said. “You can’t implement and enforce a policy with that type of error.”
Power plants are responsible for roughly 40 percent of carbon dioxide emissions nationwide. Climate-change science, air-pollution regulation and potential carbon-trading policies rely on accurate measurement of emissions. Two U.S. federal agencies — the Department of Energy and the Environmental Protection Agency — tabulate the emissions from U.S. power plants using two different methodological approaches.
The scientists analyzed those two data sets and have found that when averaged over all U.S. facilities, the median percentage difference is less than 3 percent. However, this small difference masks large differences at individual facilities.
“Power-plant emissions have been looked at for a long time, but they’re typically examined in the aggregate — ‘Here’s the whole U.S.,’” Gurney said. “They just haven’t been looked at individually or analyzed individually. That of course is where the problem arises.”
Differences that large at individual plants raise concerns over implementing the Clean Power Plan.
“This policy relies on the achievement of state-level CO2 emission-rate targets,” the authors wrote. “When examined at the state level, we find that one-third of the states have differences that exceed 10 percent of their assigned reduction amount. Such levels of uncertainty raise concerns about the ability of individual states to accurately quantify emission rates in order to meet the regulatory targets.”
It’s fixable, according to Gurney.
“It’s just that no one has paid attention,” he said. “I think that just a little bit of recalibration and consideration of good instruments, and a little more transparency from utilities, and it can fixed.”
The Clean Power Plan requires individual states to meet specific standards. Currently the plan is tied up in court; resolution is not expected this election year.
More Science and technology

ASU and Deca Technologies selected to lead $100M SHIELD USA project to strengthen U.S. semiconductor packaging capabilities
The National Institute of Standards and Technology — part of the U.S. Department of Commerce — announced today that it plans to award as much as $100 million to Arizona State University and Deca…
From food crops to cancer clinics: Lessons in extermination resistance
Just as crop-devouring insects evolve to resist pesticides, cancer cells can increase their lethality by developing resistance to treatment. In fact, most deaths from cancer are caused by the…

ASU professor wins NIH Director’s New Innovator Award for research linking gene function to brain structure
Life experiences alter us in many ways, including how we act and our mental and physical health. What we go through can even change how our genes work, how the instructions coded into our DNA are…

