ASU researcher awarded $1.25M to develop programmable, targeted drugs

Photo courtesy iStock/Getty Images
In a significant stride for medical research, Hao Yan, a professor in Arizona State University’s School of Molecular Sciences and the Biodesign Center for Molecular Design and Biomimetics, has been awarded a $1.25 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The grant, provided by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS), will fund Yan’s innovative research into programmable, targeted therapeutics.
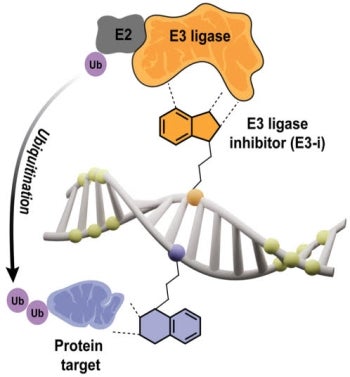
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) is a new approach in drug development that focuses on breaking down disease-causing proteins inside cells. Traditional drugs usually work by blocking the activity of specific proteins. However, about 85% of proteins in cells are considered "undruggable" with these traditional methods because they can't be effectively targeted by small-molecule drugs.
TPD therapies take a different approach by using the cell's natural system for breaking down proteins to completely remove these problematic proteins. This method is especially useful for targeting proteins that are hard to inhibit directly. One type of TPD therapy, called proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs), uses the cell's ubiquitin-proteasome system — which is like the cell's trash disposal unit — to selectively degrade these tough-to-target proteins. While PROTACs have shown promise and some are already being tested in clinical trials, there are still significant challenges and opportunities for further development in this field.
Yan’s project addresses unmet needs in targeted protein degradation therapeutics and develops a series of programmable and conditional PROTACs enabled by nucleic acid nanotechnology.
“We are excited to receive this award from NIGMS to support our programmable and conditional PROTAC platforms,” Yan said, “and we believe we could utilize the high programmability of DNA nanotechnology to address some of the unmet yet important challenges in this field.”
To improve current methods, developing an effective drug delivery system that can activate the breakdown of target proteins only under certain conditions is crucial. Nucleic acid-based techniques, which have already shown success in medicine with drugs like antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), offer great potential for advancing targeted protein degradation.
By using the natural programmability of DNA, researchers like Yan aim to create a precise way to deliver these protein-degrading therapies into cells and activate them only when needed.
More University news

3 ASU students earn Goldwater Scholarships for STEM research excellence
Three Arizona State University students have been named Goldwater Scholars for 2025, placing them among the nation’s most promising undergraduates pursuing research careers in science, engineering…

Provost Teaching Awardees, Charter Professors empower local communities, students
The ASU Charter embodies the university’s commitment to student success and research of public value and responsibility to the community. In recognition of its importance, each year, Executive…

New online Bachelor of Social Work program exceeding enrollment expectations
Social workers are in big demand.Citing U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics figures, the National Association of Social Workers projected the profession will grow 7% by 2033, faster than the average for…