Fifty years ago, Arizona State University researchers contributed to the development of medical technology that is now helping a small but growing number of patients recover from COVID-19.
The recovery of a 53-year-old Phoenix man who had been placed in a medically induced coma due to the coronavirus is one example of the benefits of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or ECMO, treatment.
The Arizona Republic, ABC15 News in Phoenix, The Hill, MedPage Today and other news outlets quoted physicians who attributed the man’s recuperation to ECMO treatment — recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for COVID-19 patients.
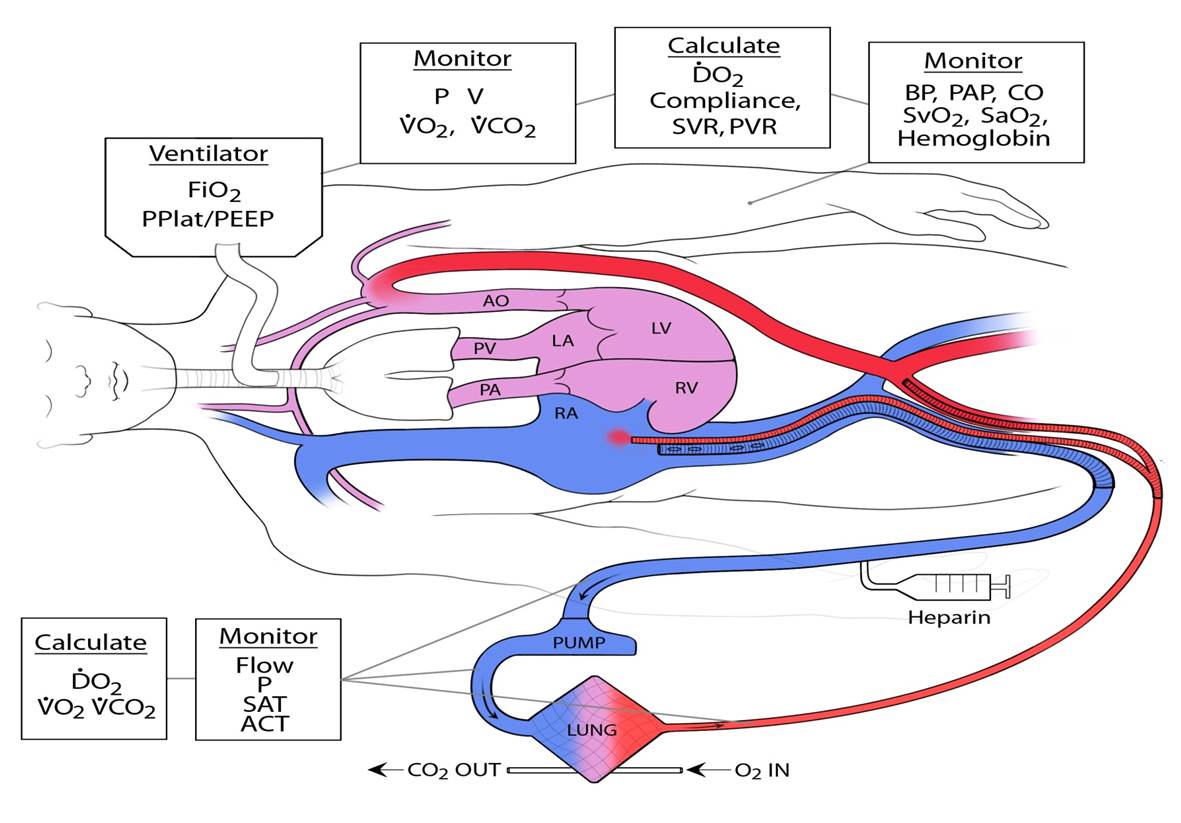
ECMO technology enables temporary replacement of heart and lung function by pumping blood outside a patient’s body, oxygenating the blood and removing carbon dioxide waste, and then returning it to the patient’s body.
The schematics of the extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or ECMO, technology shows the features of the medical device and depicts the process it performs in taking blood from the body, removing carbon dioxide waste and returning healthy blood to patients. Permission for use granted by Thomas V. Brogan, M.D., senior editor of Extracorporeal Life Support: The ELSO Red Book 5th Edition, 2017
In the late 1960s and early '70s, Arizona State University chemical engineering graduate student Keith Larsen and his mentor, the late William Dorson, helped to significantly advance research in the development of a pediatric membrane oxygenator. They then recorded the earliest attempts to use ECMO support on infants at St. Joseph’s Hospital in Phoenix.
Dorson, a professor of chemical engineering, and Larsen worked together to expand Dorson’s seminal clinical studies. They collaborated with St. Joseph’s Hospital physicians to conduct the first clinical trials of a treatment for infants who had breathing problems stemming from a lung disorder called hyaline membrane disease.
Dorson drew on his groundbreaking research on the development of artificial organs, particularly artificial lungs and kidneys, to introduce how fundamental engineering principles can directly translate into medical innovations in patients, says Vincent Pizziconi, who came to ASU in 1968 as a graduate student, working with Dorson on the design and development of an artificial kidney. Pizziconi is now an associate professor of biomedical engineering and the founder and director of the Bioengineering Design Studio in the Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering at ASU.
Dorson developed some of the country’s earliest graduate courses in biomedical engineering with the goal of training engineers to apply engineering principles to address unmet needs in health care, a legacy that continues to this day in the School of Biological and Health Systems Engineering, one of the six Fulton Schools.
“From these early beginnings of ECMO to its now widespread use for infants, children and adults with life-threatening lung and heart problems, to its recent application to patients suffering from COVID-19 who are not responding to ventilators, ECMO has had increasingly broad utility not imagined 50 years ago,” Pizziconi said.
Dorson and Larsen’s seminal work coincided with biomedical research by other scientists and practitioners around the country, particularly Robert Bartlett, a physician and medical researcher at the University of Michigan, who is known as the father of ECMO.
Applying engineering principles to meet health care needs
When he reflects on his time at ASU, Larsen, now retired, says he never imagined his early research would be a stepping stone to current ECMO devices.
Larsen recalls long periods of painstaking experimentation, working in the lab from early morning until late at night conducting a lot of trial-and-error testing.
Keith Larsen at ASU in 1971. Photo courtesy Keith Larsen
Of particular importance, Larsen studied the characteristics of straight and curved tubing for its use with the ECMO device. Because the device can transfer oxygen and carbon dioxide in the same way it is done by the lungs, Larsen used silicone rubber tubing to oxygenate the removed blood. He discovered that coils reduced the length of tubing needed in the device by more than 50%.
Larsen says he is pleased that his research was a success and proved valuable to subsequent researchers.
“I am thrilled when I hear what it is doing (in treating COVID-19 patients) and that ECMO has other medical uses.”
ECMO is also used in heart and lung transplantation. Beyond respiratory distress and failure, the treatment is sometimes used in cases of cardiac arrest, cardiogenic shock, hypothermia and septic shock.
Research collaborators respond to COVID-19 challenges
The early collaborations of Dorson, Larsen and others established with St. Joseph’s Hospital and the Barrow Neurological Institute, among other institutions, continue to pay off, Pizziconi says, pointing to ASU’s current clinical partnerships with most of the major medical centers in the Phoenix metro area, including the Barrow-ASU Initiative for Innovation in Neuro-Engineering.
In addition to Barrow and Dignity Health, which now operates St. Joseph’s Hospital, ASU has formal alliances with Mayo Clinic, Phoenix Children’s Hospital, Banner Health, Creighton University, the Maricopa Integrated Health Center and others.
Such cooperative efforts provide a platform for addressing pressing clinical needs, such as mobilizing in response to events like the COVID-19 pandemic. ASU, for instance, has created a PPE Response Network to provide personal protective equipment to hospitals and community organizations to help prevent infections.
Pizziconi says there are also discussions underway among some of the university’s biomedical engineering researchers and their collaborators on new or modified designs for ventilators to help care for COVID-19 patients.
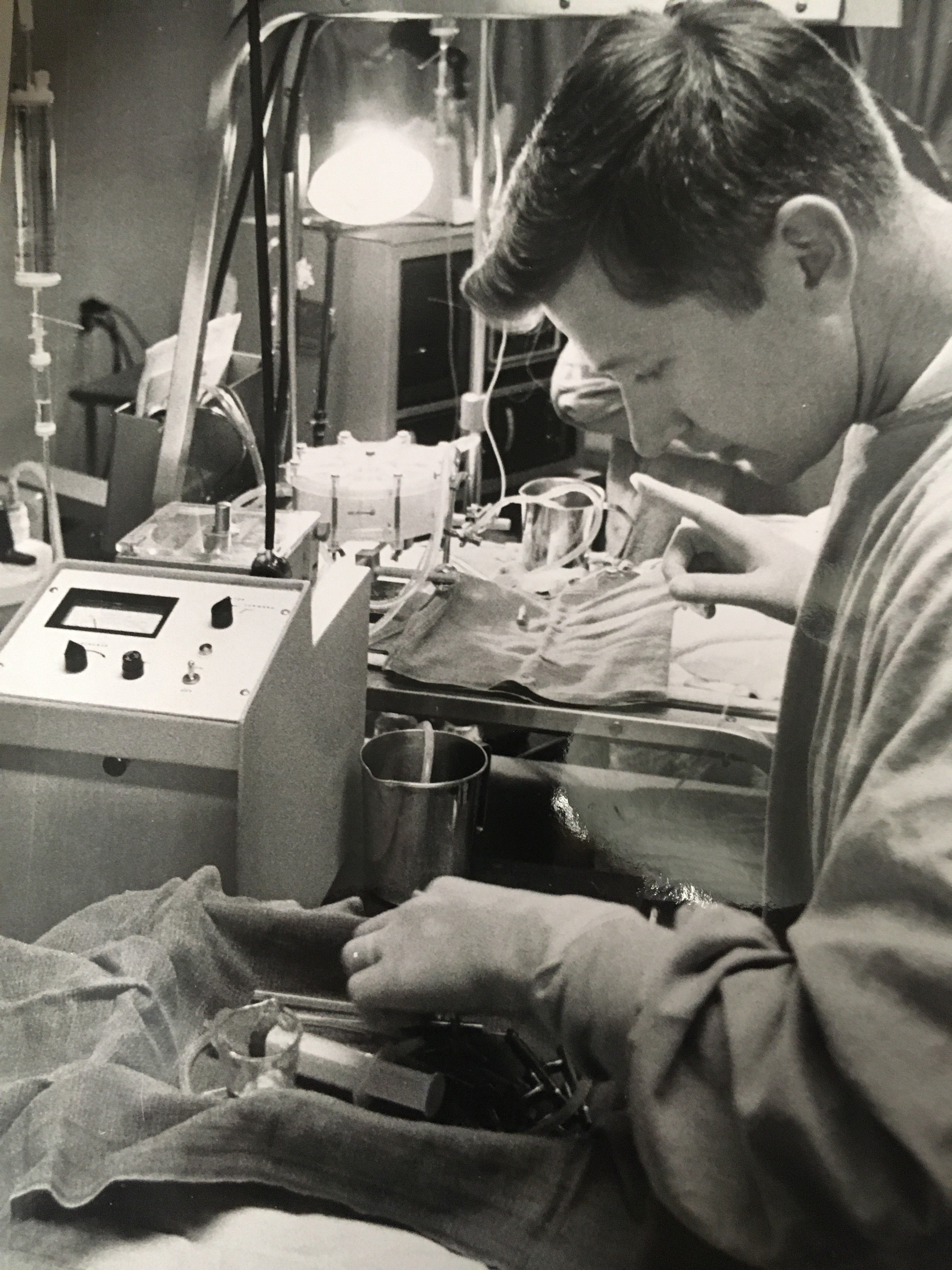
The late ASU Professor William Dorson was among the first to do research and develop technology that would lead to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or ECMO, treatment that aids patients with severe breathing problems. He is pictured at St. Joseph’s Hospital in Phoenix, applying the first ECMO treatment on infants experiencing respiratory distress. Photo courtesy of Vincent Pizziconi/ASU
Use of ECMO requires combination of resources and expertise
Health care experts caution that the technology is not a viable replacement for ventilators in all COVID-19 cases, nor is it always readily available. There are far fewer ECMO systems than ventilators, and ECMO treatments are also significantly more expensive and require an extensive commitment of health care resources to the care of individual patients.
“While it is too early to predict overall mortality and morbidity rates in those COVID-19 patients initiated on ECMO, anecdotal successes with survival to discharge have been reported in several cities in the United States and countries around the world,” said Dr. Ayan Sen, a consultant and chair of the Department of Critical Care Medicine at Mayo Clinic in Arizona.
“We performed what may have been one of the first interhospital transfer of patients to our hospital after initiating ECMO support,” Sen said.
He adds that ECMO is indeed a “resource-intensive” and complex technology, requiring a team of cardiac surgeons, nurses, intensivists and other medical specialists.
“This may be less doable in health care systems that are stressed and overwhelmed, as is evident during this pandemic,” Sen said.
Top photo: Uses of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or ECMO, technology, recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of COVID-19 patients, have expanded since its development in the 1960s and '70s. In addition to treating acute respiratory distress, it is used in cases of cardiac arrest, cardiogenic shock, hypothermia and other related conditions. Photo courtesy of Shutterstock
More Science and technology
Statewide initiative to speed transfer of ASU lab research to marketplace
A new initiative will help speed the time it takes for groundbreaking biomedical research at Arizona’s three public universities to be transformed into devices, drugs and therapies that help people.…

ASU research seeks solutions to challenges faced by middle-aged adults
Adults in midlife comprise a large percentage of the country’s population — 24 percent of Arizonans are between 45 and 65 years old — and they also make up the majority of the American workforce…

ASU research helps prevent substance abuse, mental health problems and more
Smoking rates among teenagers today are much lower than they were a generation ago, decreasing from 36% in the late 1990s to 9% today. The rates of alcohol consumption among underage drinkers…