Imagine never forgetting where you put your keys again. Or being able to weigh the odds at a blackjack table in seconds.
Having those kind of abilities sounds like something out of a Hollywood movie. In fact, the premise is one that has been explored in film many times before, including such recent movies as “Limitless” and “Lucy.”
In real life, we’ve yet to discover that magic little pill that will allow us to fully utilize our brain — but that hasn’t stopped some from trying.
So-called “brain training” programs offered by such websites as Lumosity and Cogmed have claimed that users can stave off dementia and even augment their intelligence. The training exercises consist of games that are geared toward improving an individual’s attention span and working memoryWorking memory is the ability to quickly recall information..
However, those companies have recently come under fire on charges of deceptive advertising — earlier in January, it was announced that Lumosity will pay $2 million to settle Federal Trade Commission charges — after several researchers in the field found that there was little to no evidence to support their claims of increased memory or intelligence.
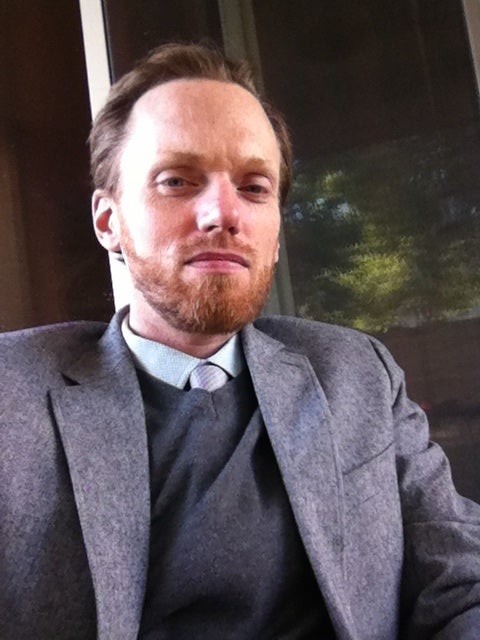
Arizona State University professor Zach ShipsteadZach Shipstead is an assistant professor in the School of Social and Behavioral Sciences, an academic unit of the New College of Interdisciplinary Arts and Sciences on Arizona State University’s West campus. (pictured left) agrees with them.
Along with colleagues, Shipstead conducted a study a few years ago on one of the games included in Lumosity’s suite of training exercises called the Dual N-Back task.
“Supposedly Dual N-Back improves working memory, improves intelligence, and we didn’t find any evidence of that, relative to a couple of different control groups,” he told HuffPost Live in a Jan. 7 Skype interview.
According to Shipstead, consumers should be cautious when it comes to the expanding market of brain-training programs because there’s just not enough evidence to show they actually work.
“There have been a lot of interesting small findings [in the field] but right now, the effects we’re producing are only large enough to be scientifically meaningful; not something that can be applied to real-world situations,” he said.
More Health and medicine

Human-centered technology embraced at ASU Digital Health Summit
Digital health technology is advancing at lightning speed, but the innovation requires a human touch to ensure that everyone benefits from the advances, according to speakers at the inaugural ASU…

Ancient DNA could help to understand recent tuberculosis outbreak in Kansas
For over a year, Wyandotte and Johnson counties in Kansas City, Kansas, have been fighting an outbreak of tuberculosis (TB) that has claimed two lives and infected nearly 150 residents. The…

ASU researchers propose unifying model of Alzheimer’s disease
In a groundbreaking theory, scientists at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute propose a unifying explanation for the molecular chaos driving Alzheimer's disease. The condition causes…